The Endocannabinoid System
Why cannabis affects people the way it does?
Highlights:
- Cannabis plants and humans share a chemical trait: the presence of cannabinoids in our chemistry.
- Humans have an endocannabinoid system that is directly affected by the cannabinoids in cannabis when it’s consumed.
- The effect of this interaction is different for everyone.
The way in which the phytocannabinoids in cannabis interact within the body’s Endocannabinoid System can produce a range of temporary effects on the mind and/or body. The effects vary from person to person and depend on many factors, including an individual’s physiology, the strain, how it’s consumed, how much is consumed and the THC/CBD content.
Cannabinoids: The Link Between Cannabis and Humans
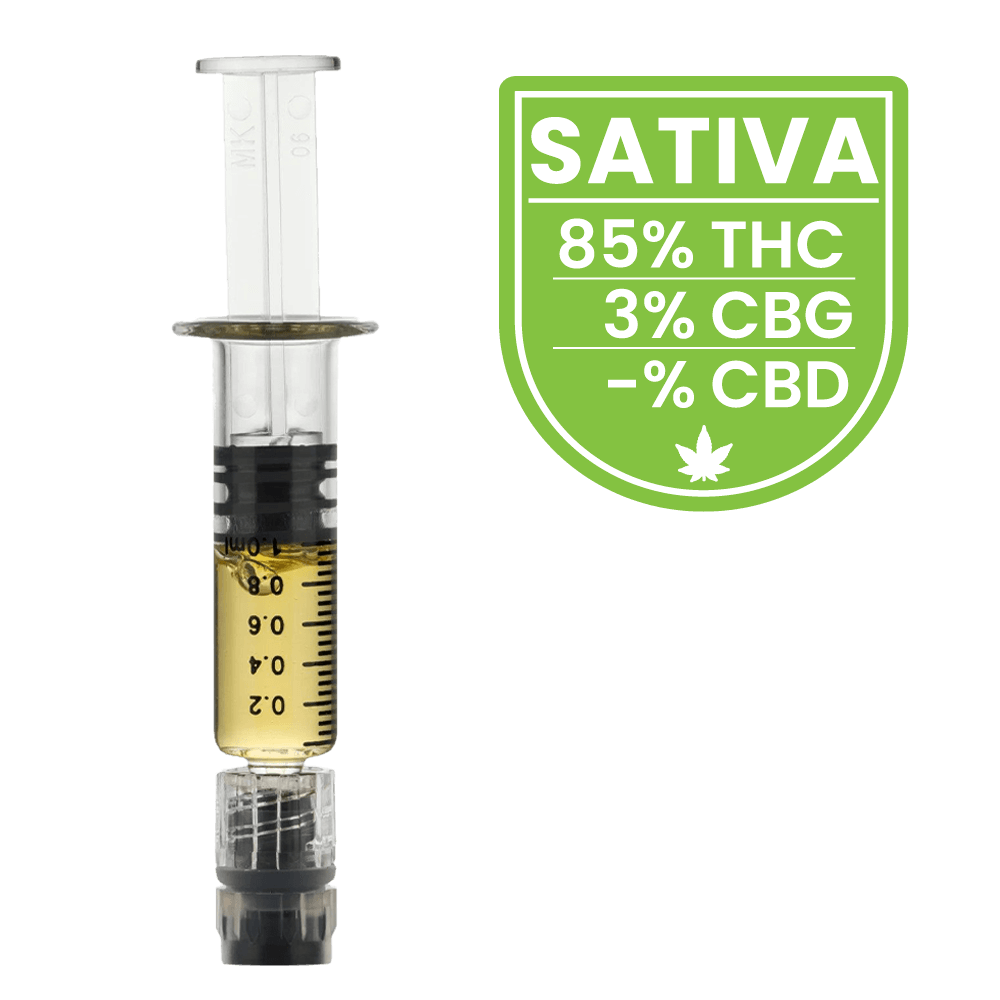
Both cannabis plants and people have chemical compounds in our systems called cannabinoids. In humans, they’re called endocannabinoids. In plants, they’re called phytocannabinoids. The cannabis plant has many cannabinoids, of which the two best known and studied are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
THC is responsible for the way your brain and body respond to cannabis, including the psychoactive effect, or “high,” and the associated physical impairment.
Unlike THC, CBD does not generally produce a “high.” There is some evidence that CBD may block or lower some of the effects of THC on the brain when the amount of CBD in a product is the same as or higher than the amount of THC.
Humans produce cannabinoids internally through an important system in our bodies called the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Studies suggest the ECS plays a role in regulating stress recovery, nervous system protection, immune system response and homeostatic balance (our overall state of optimal health function and stability). Our endocannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors all over our bodies to help regulate those functions.
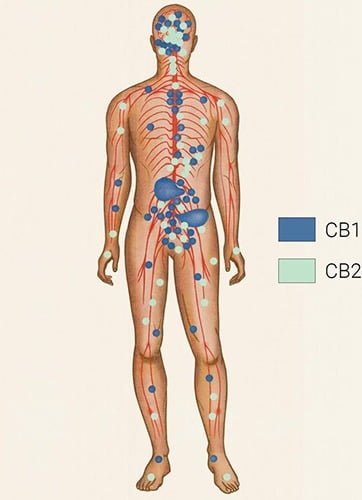
Humans have two types of receptors: CB1 and CB2. Receptor sites are found in many organs and areas of the body, but CB1 receptors are primarily located in the central nervous system, which includes the brain. CB2 receptors are found primarily in the immune system.
When cannabis is consumed, cannabinoids like THC and CBD can interact with our receptor sites like our own endocannabinoids do. It is because many of those receptor sites are located in the central nervous system that cannabis is likely to produce changes to our cognitive and/or physical states.
The response to cannabis is completely individual
Everyone’s physiological makeup is different, and the ECS receptor site locations and the number of sites can vary from person to person. That is why the same strain of cannabis can affect people differently. Additional factors that contribute to the potential differences in effect can also include the genetics, gender, current health, personality and age of the individual.
Being aware of this unique interaction between cannabis and the human body is helpful in understanding how to make the right choice for you.
If you’re new to consuming cannabis, consider starting at very low THC and CBD levels as you learn how your body responds.